What Stock market is:
A stock market is very well known to all as a share market or the equity market. Here buyers and sellers aggregate stocks (shares), which represent ownership claims on businesses; these may include securities listed on a public stock exchange, as well as stock that is only traded privately, such as shares of private companies that are sold to investors through equity crowdfunding platforms. most often, Investment in the stock market is done via stock brokerages in electronic trading platforms. Investment usually needs an investment strategy in mind.
Stocks can be categorized where the company is domiciled by the country. For example, Reliance and SBIN are domiciled in India and traded on the NSE and BSE, so they may be considered as part of the Indian stock market, although the stocks may also be traded on exchanges in other countries, for example, as American depositary receipts (ADRs) on U.S. stock markets.
Size of the Stock markets
From the year 1980 to the end of 2018, the total market capitalization of equity-backed securities worldwide rose from US$2.5 trillion to US$68.65 trillion. As of New Year’s Eve, 2019, the entire market capitalization of all stocks worldwide was approximately US$70.75 trillion.
From the year 1980 to the end of 2018, the total market capitalization of equity-backed securities worldwide rose from US$2.5 trillion to US$68.65 trillion. As of New Year’s Eve, 2019, the entire market capitalization of all stocks worldwide was approximately US$70.75 trillion.
The largest stock exchange as of January’20 is The US of America (about 54.5%), followed by Japan (about 7.7%) and therefore the UK (about 5.1%).
Stock exchange
A stock exchange is an exchange where Many large companies have their stocks listed. Stockbrokers and traders can buy as well as sell shares of stock, bonds, and other securities there on a stock exchange. Which makes the stock more liquid and thus more attractive to many investors. The exchange may also remain as a guarantor of settlement. Other stocks may be traded “over the counter” (OTC) through a dealer.
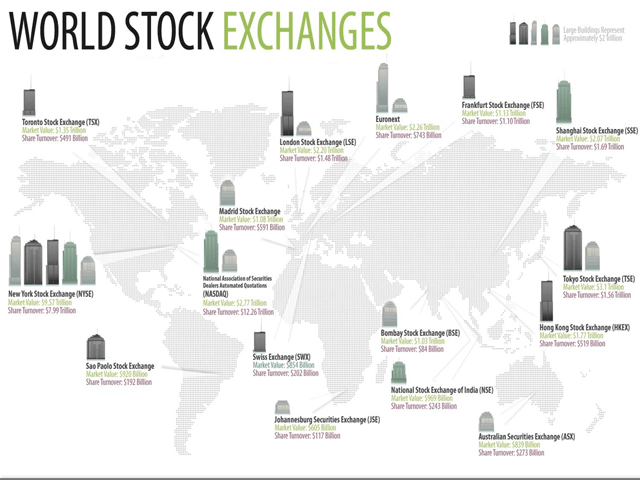
Some large companies will have their stock listed on more than one exchange in different countries, so as to play a role in attracting international investors.
Stock exchanges can also cover other sorts of securities, like fixed interest securities (bonds) or (less frequently) derivatives which are more likely to be traded OTC.
Trade-in stock markets mean the exchange of stock for the transfer of money or security from a buyer to a seller. This requires both buyer and seller to agree on a price. Equities/stocks (shares) confer an ownership interest in a particular company.
Based on anywhere in the world, may Participants in the stock market range from small individual stock investors to larger investors, and may include banks, insurance companies, pension funds, and hedge funds. Their buy or sell orders will be executed on their behalf by a stock exchange trader.
Physical locations may be there in some exchanges where transactions are carried out on a trading floor, by a method known as open outcry. This method is employed in some stock exchanges and commodities exchanges and involves traders shouting bid and offer prices. But the other type of stock exchange has a network of computers where trades are done electronically. An example of such an exchange is that the NASDAQ.
A potential seller asks a specific price for a stock, and a potential buyer bids a specific price for the same stock. Buying or selling at the market happens while you will accept any ask price or bid price for the stock. A sale takes place when the bid and ask prices match. Trading bases on a first-come, first-served, if there are multiple bidders at a given price.
The Facilitation of exchanging securities between buyers and sellers is the purpose of a stock exchange, thus providing a marketplace. The exchanges provide real-time trading information on the listed securities and facilitate price discovery.
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) is one of the examples of a physical exchange, with a hybrid market for placing orders electronically from any location as well as on the trading floor. Orders executed on the floor enter by way of exchange members and flow right down to a floor broker, they submit the order electronically to the ground country store to trade for that stock, for the order the “DMM” (Designated market maker). The job of DMM’s is to maintain a two-sided market, making orders such as buying and selling the security when there are no other buyers or sellers.
If a bid-ask spread exists, no trade immediately takes place – during this case, the DMM may use their own resources (money or stock) to shut the difference. Once a trade has been made, the small print is reported on the “tape” and sent back to the brokerage, which then notifies the investor who placed the order. But Computers play an important role in program trading.
For instance, The NASDAQ is an electronic exchange, where all of the tradings is done over a computer network. The process is very similar to the New York Stock Exchange. One or more NASDAQ market makers will always provide a bid and ask price at which they’re going to always purchase or sell ‘their’ stock.
A part of Euronext, The Paris Bourse is an order-driven, electronic stock exchange. Which was automated in the late 1980s. Since then, it consisted of an open outcry exchange. Stockbrokers met on the floor of the Palais Brongniart. The CATS trading system was introduced In 1986, and the order matching system was fully automated then.
People will prefer to trade stock on the most popular exchange since this gives the largest number of potential counterparties and probably the best price. However, there have always been alternatives like brokers trying to bring parties together to trade outside the exchange
To read my article on “10 major options of investment” click here


Comments are closed.